1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
|
import json
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Model, Input
from keras.layers import Dense, Bidirectional, Dropout, LSTM, TimeDistributed, Masking
from keras.utils import to_categorical, plot_model
from seqeval.metrics import classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from utils import event_type
from utils import MAX_SEQ_LEN, train_file_path, test_file_path, dev_file_path
from load_data import read_data
from albert_zh.extract_feature import BertVector
bert_model = BertVector(pooling_strategy="NONE", max_seq_len=MAX_SEQ_LEN)
f = lambda text: bert_model.encode([text])["encodes"][0]
with open("%s_label2id.json" % event_type, "r", encoding="utf-8") as h:
label_id_dict = json.loads(h.read())
id_label_dict = {v:k for k,v in label_id_dict.items()}
def input_data(file_path):
sentences, tags = read_data(file_path)
print("sentences length: %s " % len(sentences))
print("last sentence: ", sentences[-1])
print("start ALBERT encding")
x = np.array([f(sent) for sent in sentences])
print("end ALBERT encoding")
new_y = []
for seq in tags:
num_tag = [label_id_dict[_] for _ in seq]
if len(seq) < MAX_SEQ_LEN:
num_tag = num_tag + [0] * (MAX_SEQ_LEN-len(seq))
else:
num_tag = num_tag[: MAX_SEQ_LEN]
new_y.append(num_tag)
y = np.empty(shape=(len(tags), MAX_SEQ_LEN, len(label_id_dict.keys())+1))
for i, seq in enumerate(new_y):
y[i, :, :] = to_categorical(seq, num_classes=len(label_id_dict.keys())+1)
return x, y
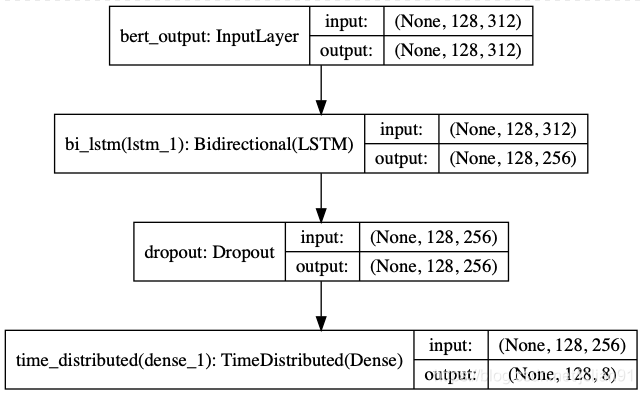
def build_model(max_para_length, n_tags):
bert_output = Input(shape=(max_para_length, 312, ), name="bert_output")
lstm = Bidirectional(LSTM(units=128, return_sequences=True), name="bi_lstm")(bert_output)
drop = Dropout(0.1, name="dropout")(lstm)
out = TimeDistributed(Dense(n_tags, activation="softmax"), name="time_distributed")(drop)
model = Model(inputs=bert_output, outputs=out)
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
plot_model(model, to_file="albert_bi_lstm.png", show_shapes=True)
return model
def train_model():
train_x, train_y = input_data(train_file_path)
dev_x, dev_y = input_data(dev_file_path)
test_x, test_y = input_data(test_file_path)
model = build_model(MAX_SEQ_LEN, len(label_id_dict.keys())+1)
history = model.fit(train_x, train_y, validation_data=(dev_x, dev_y), batch_size=32, epochs=10)
model.save("%s_ner.h5" % event_type)
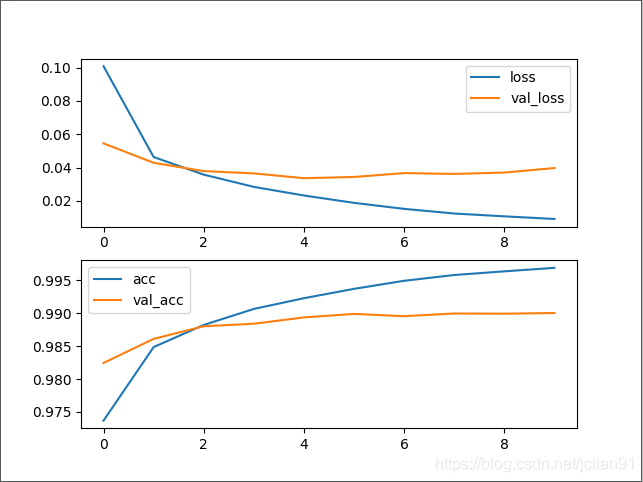
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
epochs = len(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(range(epochs), history.history['loss'], label='loss')
plt.plot(range(epochs), history.history['val_loss'], label='val_loss')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
epochs = len(history.history['acc'])
plt.plot(range(epochs), history.history['acc'], label='acc')
plt.plot(range(epochs), history.history['val_acc'], label='val_acc')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig("%s_loss_acc.png" % event_type)
y = np.argmax(model.predict(test_x), axis=2)
pred_tags = []
for i in range(y.shape[0]):
pred_tags.append([id_label_dict[_] for _ in y[i] if _])
test_sents, test_tags = read_data(test_file_path)
final_tags = []
for test_tag, pred_tag in zip(test_tags, pred_tags):
if len(test_tag) == len(pred_tag):
final_tags.append(pred_tag)
elif len(test_tag) < len(pred_tag):
final_tags.append(pred_tag[:len(test_tag)])
else:
final_tags.append(pred_tag + ['O'] * (len(test_tag) - len(pred_tag)))
print(classification_report(test_tags, final_tags, digits=4))
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_model()
|