NLP(四十五)R-BERT在人物关系分类上的尝试及Keras代码复现
本文将介绍关系分类模型R-BERT和该模型在人物关系数据集上的表现,以及该模型的Keras代码复现。
关系分类任务
关系分类属于NLP任务中的文本分类,不同之处在于,关系分类提供了文本和实体。比如下面的例子:
亲戚 1837年6月20日,
威廉四世 辞世,他的侄女维多利亚 即位。
其中两个实体在文本中用
在关系分类中,我们要注重文本特征,更要留意实体特征。常见的英文关系分类的数据集为SemEval 2010 Task 8、New York Times Corpus、WikiData dataset for Sentential Relation Extraction、NYT29、NYT24等,中文的关系分类数据集比较少,而且质量不高。
关于SemEval 2010 Task 8数据集的实现模型及效果,可以参考:http://nlpprogress.com/english/relationship_extraction.html, 其中常见的实现模型如下:
Machince Learning: SVM, Word2Vec ...
Dependency Models: BRCNN, DRNN ...
CNN-based Models: Multi-Attention CNN, Attention CNN, PCNN+ATT ...
BERT-based Models: R-BERT, Matching-the-Blanks ...
本文将介绍
R-BERT模型。
模型介绍
R-BERT模型是Alibaba Group (U.S.)
Inc的两位研究者在2019年5月的论文Enriching Pre-trained
Language Model with Entity Information for Relation
Classification,该模型在SemEval 2010 Task
8数据集上的F1值为89.25%,只比现有的SOTA模型低了0.25%。
R-BERT很好地融合了文本特征以及两个实体在文本中的特征,简单来说,该模型主要是BERT模型中的三个向量的融合:
[CLS]对应的向量
实体1的平均向量
实体2的平均向量
下面将详细讲解
R-BERT的具体模型结构。
模型结构
R-BERT的具体模型结构如下图:
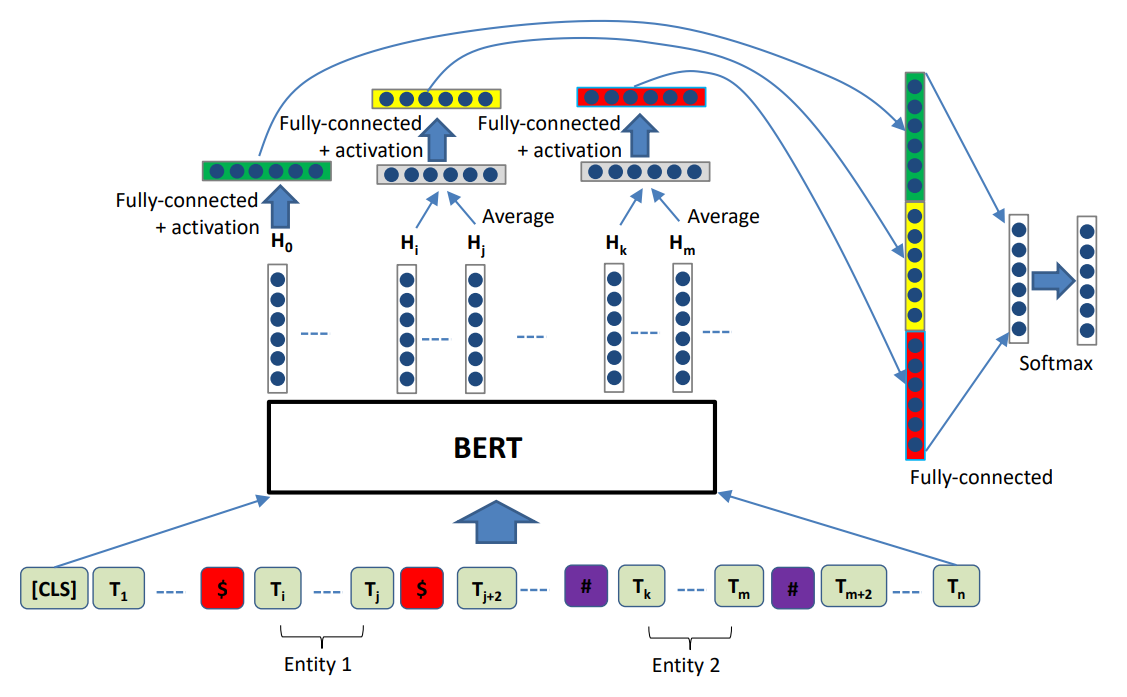
一图胜千言。从上述的模型结构图中,我们将模型结构分解步骤如下:
- 将文本接入BERT模型,获取[CLS] token的对应向量、实体1的在BERT输出层中的平均向量、实体2的在BERT输出层中的平均向量;
- 将上述三个向量分别接Drouput层、Tanh激活层以及全连接层;
- 再将步骤2输出的三个向量进行拼接(concatenate);
- 最后接Dropout层和全连接层,用Softmax作为多分类的激活函数。
此外,需要注意的是,输入文本中没有[SEP]这个token。
论文中并没有给出更多的实现细节,需要深入到代码中去查看。网上已经有人给出了Torch框架的实现R-BERT的代码,参考网址为:https://github.com/monologg/R-BERT。
Torch实现
Torch框架的实现R-BERT的代码(模型部分)如下:
1 | |
该项目是在SemEval 2010 Task 8数据集实现的,笔者将其在自己的人物关系分类数据集上进行测试,最终在测试集上的评估结果如下:
1 | |
Model: chinese-roberta-wwm-ext-large, 详细的评估结果如下:
1 | |
R-BERT模型在人物关系数据集上的Github项目为R-BERT_for_people_relation_extraction
。下面将介绍R-BERT模型的Keras框架复现。
Keras复现
R-BERT模型的Keras框架复现(模型部分)的代码如下:
1 | |
总结
R-BERT模型再次见证了BERT等预训练模型的强大。该模型的实现思路比较简单,也取得了很不错的效果,是关系分类任务的一大突破。
当然对笔者来说,也有种重要的意义:第一次自己复现了论文代码,虽然有Torch代码可以参考。
本文分享到此结束,感谢阅读~
2021年4月1日于上海杨浦,此日大雾迷城~
参考文献
- NLP-progress Relation Extraction: http://nlpprogress.com/english/relationship_extraction.html
- Huggingface Transformers: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
- https://github.com/wang-h/bert-relation-classification
- R-BERT: https://github.com/monologg/R-BERT
- Enriching Pre-trained Language Model with Entity Information for Relation Classification: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.08284.pdf
- Chinese-BERT-wwm: https://github.com/ymcui/Chinese-BERT-wwm

欢迎关注我的知识星球“自然语言处理奇幻之旅”,笔者正在努力构建自己的技术社区。
